By Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life
Global Restrictions on Religion Executive Summary
For more than half a century, the United Nations and numerous international organizations have affirmed the principle of religious freedom. For just as many decades, journalists and human rights groups have reported on persecution of minority faiths, outbreaks of sectarian violence and other pressures on religious individuals and communities in many countries. But until now, there has been no quantitative study that reviews an extensive number of sources to measure how governments and private actors infringe on religious beliefs and practices around the world.
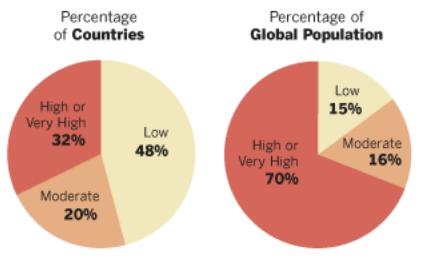
(Numbers may not add up to 100% due to rounding)
Global Restrictions on Religion
Global Restrictions on Religion, a new study by the Pew Research Center’s Forum on Religion & Public Life, finds that 64 nations – about one-third of the countries in the world – have high or very high restrictions on religion. But because some of the most restrictive countries are very populous, nearly 70 percent of the world’s 6.8 billion people live in countries with high restrictions on religion, the brunt of which often falls on religious minorities.
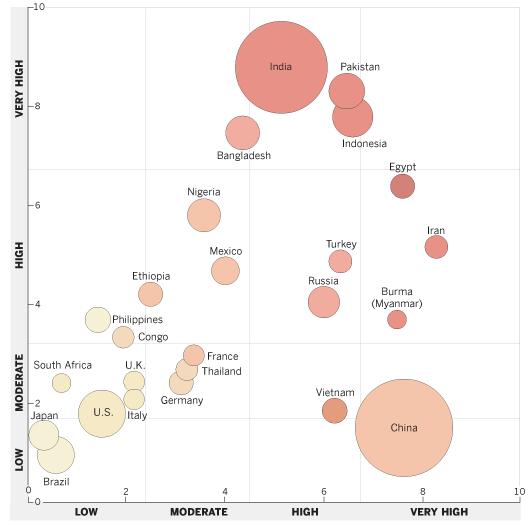
Some restrictions result from government actions, policies and laws. Others result from hostile acts by private individuals, organizations and social groups. The highest overall levels of restrictions are found in countries such as Saudi Arabia, Pakistan and Iran, where both the government and society at large impose numerous limits on religious beliefs and practices. But government policies and social hostilities do not always move in tandem. Vietnam and China, for instance, have high government restrictions on religion but are in the moderate or low range when it comes to social hostilities. Nigeria and Bangladesh follow the opposite pattern: high in social hostilities but moderate in terms of government actions.
Among all regions, the Middle East-North Africa has the highest government and social restrictions on religion, while the Americas are the least restrictive region on both measures. Among the world’s 25 most populous countries, Iran, Egypt, Indonesia, Pakistan and India stand out as having the most restrictions when both measures are taken into account, while Brazil, Japan, the United States, Italy, South Africa and the United Kingdom have the least.
25 Most Populous Countries Teaser
The Pew Forum’s study examines the incidence of many specific types of government and social restrictions on religion around the world. In 75 countries (38%), for example, national or local governments limit efforts by religious groups or individuals to persuade others to join their faith. In 178 countries (90%), religious groups must register with the government for various purposes, and in 117 (59%) the registration requirements resulted in major problems for, or outright discrimination against, certain faiths.
Public tensions between religious groups were reported in the vast majority (87%) of countries in the period studied (mid-2006 through mid-2008). In 126 countries (64%), these hostilities involved physical violence. In 49 countries (25%), private individuals or groups used force or the threat of force to compel adherence to religious norms. Religion-related terrorism caused casualties in 17 countries, nearly one-in-ten (9%) worldwide.
These are some of the key findings of Global Restrictions on Religion. The study covers 198 countries and self-administering territories, representing more than 99.5% of the world’s population. In preparing this study, the Pew Forum devised a battery of measures, phrased as questions, to gauge the levels of government and social restrictions on religion in each country. To answer these questions, Pew Forum researchers combed through 16 widely cited, publicly available sources of information, including reports by the U.S. State Department, the U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom, the U.N. Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Religion or Belief, the Council of the European Union, the United Kingdom’s Foreign & Commonwealth Office, Human Rights Watch, the International Crisis Group, the Hudson Institute and Amnesty International. (The complete list of sources is available in the Methodology.)
The researchers involved in this process recorded only factual reports about government actions, policies and laws, as well as specific incidents of religious violence or intolerance over the main two-year period covered by this study, from mid-2006 to mid-2008. . . .
Limitations of the Study
It is important to keep a few caveats in mind when reading this report. First, because freedom – defined as “the absence of hindrance, restraint, confinement or repression” – is difficult if not impossible to measure, the Pew Forum’s study instead measures the presence of restrictions of various kinds. The study tallies publicly reported incidents of religious violence, intolerance, intimidation and discrimination by governments and private actors. That is, it focuses on the problems in each country. It does not capture the other side of the coin: the amount of religious dynamism, diversity and expression in each country. The indexes of government restrictions and social hostilities are intended to measure obstacles to the practice of religion. But they are only part of a bigger picture.
Second, this study does not attach normative judgments to restrictions on religion. Every country studied has some restrictions on religion, and there may be strong public support in particular countries for laws aimed, for example, at curbing “cult” activity (as in France), preserving an established church (as in the United Kingdom) or keeping tax-exempt religious organizations from endorsing candidates for elected office (as in the United States). The study does not attempt to determine whether particular restrictions are justified or unjustified. Nor does it attempt to analyze the many factors – historical, demographic, cultural, religious, economic and political – that might explain why restrictions have arisen. It seeks simply to measure the restrictions that exist in a quantifiable, transparent and reproducible way, based on reports from numerous governmental and nongovernmental organizations.
Finally, because North Korean society is effectively closed to outsiders and independent observers lack regular access to the country, the sources are unable to provide the kind of specific, timely information . . . for this quantitative study. Therefore, the report does not include scores for North Korea.
Disclaimer: Articles featured on Oregon Report are the creation, responsibility and opinion of the authoring individual or organization which is featured at the top of every article.